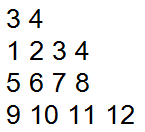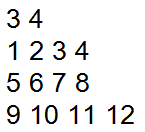Main content:
An introduction to threads
How to create threads
How to manipulate threads
How to synchronize threads
The Order Queue application
-------------------
1. An introduction to threads
2. How to create threads
3. How to manipulate threads
4. How to synchronize threads
5. The Order Queue application
Bài tập:
1. Dùng thread viết chương trình cứ mỗi giây in giá trị một biến đếm tăng dần ra màn hình. Ví dụ bên dưới:
Dem: 0
Dem: 1
Dem: 2
Dem: 3
...
Mã nguồn:
Cách 1: extends từ Thread
Cách 2: implements từ Runnable
2. Viết chương trình tạo 2 thread:
- Với thread thứ nhất sau mỗi giây in ra giá trị của một số nguyên tăng dần (int count1).
- Với thread thứ hai sau mỗi giây in ra 2 lần giá trị của một số nguyên tăng dần (int count2).
Mã nguồn:
4.
An introduction to threads
How to create threads
How to manipulate threads
How to synchronize threads
The Order Queue application
-------------------
1. An introduction to threads
2. How to create threads
Ví dụ:
3. How to manipulate threads
4. How to synchronize threads
5. The Order Queue application
Bài tập:
1. Dùng thread viết chương trình cứ mỗi giây in giá trị một biến đếm tăng dần ra màn hình. Ví dụ bên dưới:
Dem: 0
Dem: 1
Dem: 2
Dem: 3
...
Mã nguồn:
Cách 1: extends từ Thread
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread t2 = new IOThread();
t2.start();
}
}
class IOThread extends Thread {
int dem = 0;
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Dem: " + dem++);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch
(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Cách 2: implements từ Runnable
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread t = new Thread (new IOTask());
t.start();
}
}
class IOTask implements Runnable {
int dem = 0;
public void run() {
while(true) {
System.out.println("Dem:" + dem++);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch
(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. Viết chương trình tạo 2 thread:
- Với thread thứ nhất sau mỗi giây in ra giá trị của một số nguyên tăng dần (int count1).
- Với thread thứ hai sau mỗi giây in ra 2 lần giá trị của một số nguyên tăng dần (int count2).
Kết quả in ra màn hình như sau:
Thread 1: count1 = 0
Thread 2: count2 = 0
Thread 2: count2 = 1
Thread 1: count1 = 1
Thread 2: count2 = 2
Thread 2: count2 = 3
Thread 1: count1 = 2
Thread 2: count2 = 4
Thread 2: count2 = 5
...
...
Mã nguồn:
3. Viết chương trình demo sử dụng synchronized:
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Thread1 t1 = new Thread1();
t1.start();
Thread2 t2 = new Thread2();
t2.start();
}
}
class Thread1 extends Thread {
int count1 = 0;
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Thread 1:
count1 = " + count1++);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch
(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Thread2 extends Thread {
int count2 = 0;
public void run() {
while(true) {
System.out.println(" Thread 2: count2 = " + count2++);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch
(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Mã nguồn:
//example of java
synchronized method
class Table {
synchronized void printTable(int n) {// synchronized
method
for (int i = 1; i <= 5;
i++) {
System.out.println(n * i);
try {
Thread.sleep(400);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
}
class MyThread1 extends Thread {
Table t;
MyThread1(Table t) {
this.t = t;
}
public void run() {
t.printTable(5);
}
}
class MyThread2 extends Thread {
Table t;
MyThread2(Table t) {
this.t = t;
}
public void run() {
t.printTable(100);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Table obj = new Table();// only one object
MyThread1 t1 = new MyThread1(obj);
MyThread2 t2 = new MyThread2(obj);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
4.
 7/29/2015 05:06:00 CH
7/29/2015 05:06:00 CH